
Whitespace is optionally trimmed from content then re-inserted on download for convenience so that translators do not have to manage the extra spaces. With this directive, you can trim whitespaces, as it enables or disables whitespace trim management for the ingested strings. When rendered, a whitespace character is not a visible mark, but does occupy an area or space on a page.Īlthough whitespaces are necessary within a string (typically to separate words), unnecessary whitespaces can be found at the start of a string (leading) and at the end of a string (trailing).
Madcap support series#
On | yes | true or off | no | false or leading| trailingĪ whitespace is any character or series of characters that represent horizontal or vertical space in typography. Numerical entities are not considered at all with this directive, and are treated normally. This does not affect source content at all - so using it will not result in new strings.
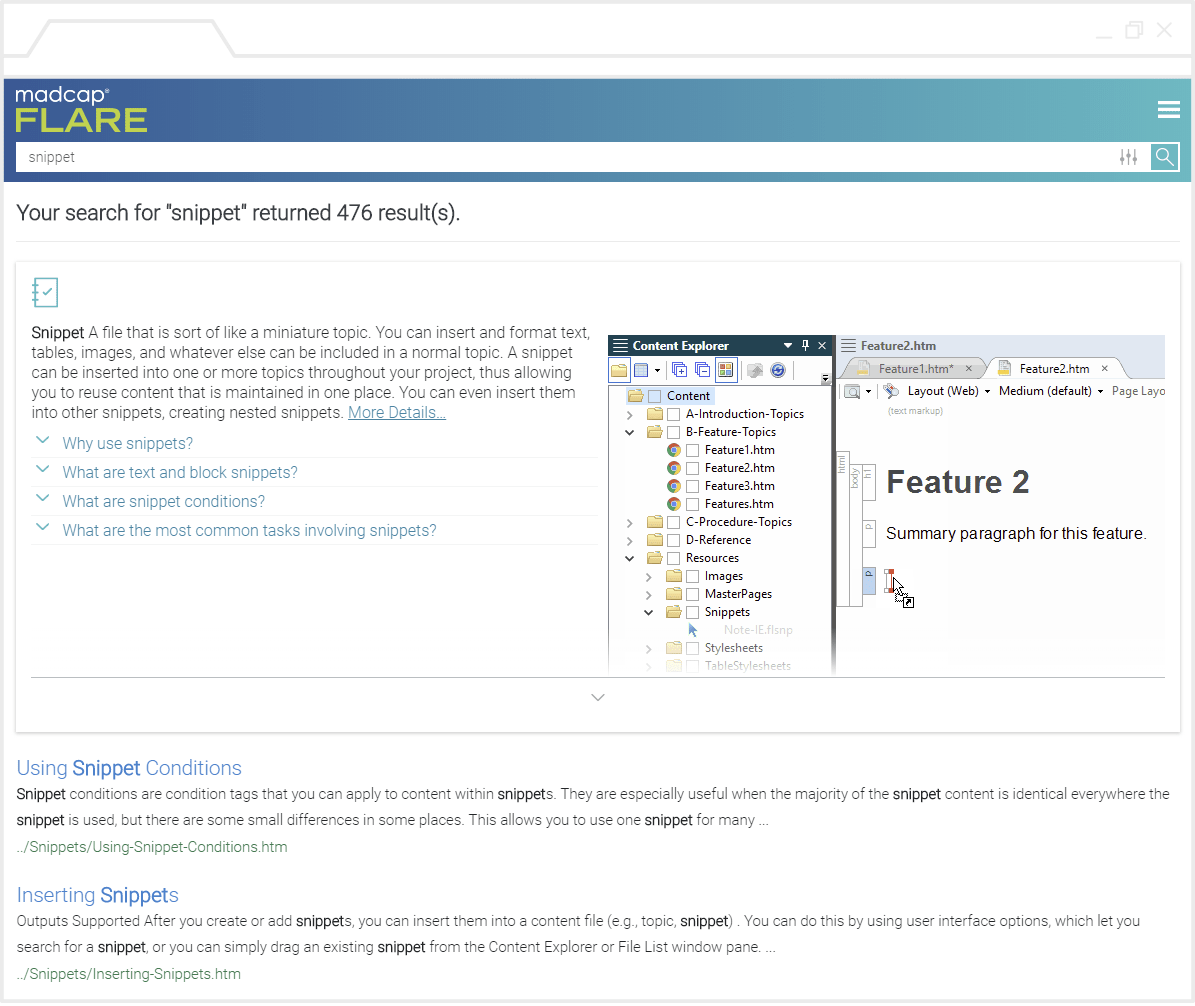
This directive can be placed inline, in the API or in a template (consult your SA about configuring directive templates). However, if there are a different number of characters in the translation where the translation process removed or added some and the escaping is inconsistent among them, propagate will escape all entities for that character. If the same character is both escaped and unescaped in the same string, propagate will return the characters in the translation escaped in the same order as they were in the source. Base entities continue to be controlled by HTML detection and the entity_escaping directive.
Propagate will only affect non-base entities - all named entities except &, ', <, >.The default is none which is the current behavior, which recognizes HTML4 entities only - if HTML5 entities are required as well, you must use the entity_escaping_type=propagate directive. For each entity character, we'll check to see if it was escaped in the source and try to match (propagate) it in the target.
Madcap support update#
For example, normally we turn © into © but if we use this new directive the translation will automatically update to use escaping from the source. Used to retain entity escaping for all non-base entities. XML Characters (always escaped) Character (name) Using will allow This is an & " example string4 to appear unescaped.

When the translated file is downloaded, the translated string will be escaped as: Valuesįor example, your translation might look like this:īy default, using the "auto" setting, we will assume this is HTML from the tag.

entity_escapingĮxact delivery depends on file type. Here are some examples of, along with example values or paths. Directives are specified in comments within the files, in the following format: Inline File Format ĪPI Parameter smartling. Directivesįile directives are supported, both inline and via our API.
Madcap support archive#
Non-XLIFF files in the archive are excluded from processing.ĭirectory structure and non-XLIFF files are preserved when downloading the translated archive. zip file, not the individual XLIFF files. Translated strings in the archive will be associated with the. A MadCap archive is treated as a single file.

Smartling supports Madcap Lingo version 10.Ī MadCap package is a ZIP-archive with one or more XLIFF files, optionally organized in directories.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
